The Assign sub menu allows to map the symbolic reference LAN and WAN to the physical interfaces that are present on the system. Click on the Save button to apply changes, and remember that a change in this assignment will require a system reboot for the changes to take effect.
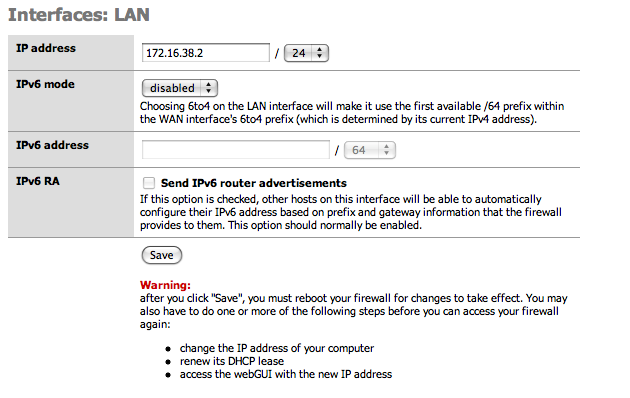
In the LAN section, it is possible to change the IP address and the netmask (in CIDR notation) of the firewall internal interface. The system must be rebooted in order to apply the changes as suggested after pressing the "Save" button.

In the WAN sub section, it is possible to set up all the parameters for WAN interface. The WAN Interface can be a Static IP address, a DHCP address, a PPPoE interface or a PPTP connection, as detailed in the following. On the basis of the connection type selected, the related sub panel must be filled.
A detailed description of all the fields follows.
-
Type: the connection type that must be used
Static: A static IP address is assigned to the interface with the related netmask and gateway
DHCP: a dynamic address is assigned to the firewall WAN by a DHCP server on the WAN side
PPPoE: PPP over Ethernet, that is useful for ADSL connection
PPTP: allows to set up PPTP for the ADSL providers that requires this protocol for the connection
-
General Configuration Panel: allow to override default MAC address and MTU
MAC Address: Some cable connections require the MAC spoofing. The MAC address must be in the format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
-
MTU: This was moved to the PPPoE section, and only works for PPPoE now. It is left here in the documentation because it may be moving back.
The value in this field allows to set up MSS clamping for TCP connections to the value entered above minus 40 (TCP/IP header size). If the field is left blank, an MTU of 1492 bytes for PPPoE and 1500 bytes for all other connection types will be assumed
-
Static IP Configuration: in this panel the static IP and gateway for WAN interface must be set:
IP Address: the static IP with related netmask is set in this field
Gateway: the default gateway for the firewall in set in this field
-
PPPoE Configuration: The Username and password for the ADSL connection should be set up there
Username: the username the provider assign to your connection
Password: the password the provider assign to your connection
-
PPTP Configuration: the parameters inserted in this sub panel allows the user to establish the tunnel required by the PPTP ADSL connection
Username: the username the provider assign to your connection
Password: the password the provider assign to your connection
Local IP Address: the local IP address the provider assign to your connection
Remote IP Address: the remote IP address the provider assign to your connection
Block Private Networks - This option puts in rules to drop traffic coming in on the WAN from private IP subnets. If you configure your SmallWall with the WAN interface on a private subnet of another LAN, for example, you need to disable this option. Also, some ISP's assign customers private IP's, in which case you'll also need to disable this option
Note
You do not need to disable the Block Private Networks option if you are using IPsec VPN tunnels with private IP addresses. When the VPN packets come into the WAN interface, they will be coming from source IP of the WAN interface of the remote VPN device, not from the private IP subnet on the remote side.
Optional interfaces can be used for a variety of purposes. Generally they are used as second LAN interfaces or DMZ interfaces.
The wireless interface configuration screen is only presented if a compatible wireless card is found at system startup. Options will be presented depending on the features supported for the wireless card. See the Wireless chapter for more information on wireless configuration options.